The VSP of this example shows a high level of tube waves labeled TW1 to TW6. The surface waves generated by the source create a field of tube waves (TW1 in green) that is reflected at the well bottom (TW2 in red) and at the top of a porous and permeable zone located at a depth of 440 m (TW3 in blue). TW3 is again reflected at the surface, on the fluid-air contact (TW4 in khaki). As it enters the permeable zone at 440 m, the downgoing P wave creates a tube wave (TW5 in orange), which is reflected at the bottom of the well (TW6 in purple). One can also note the presence of secondary tube waves with a low apparent velocity; these are due to the geophone itself.
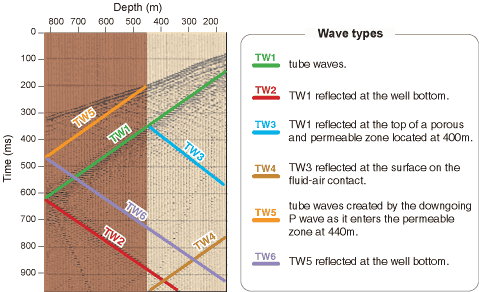
![]() Example of VSP with tubed waves
Example of VSP with tubed waves
(document : Gaz de France - IFP)
Sometimes, Stoneley waves can be used to obtain information on the velocity of shear waves and the permeability of the formations encountered by the well.