Liquid junction potential
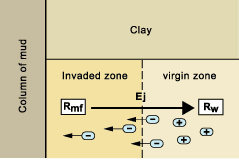
Another natural electromotive force appears in the boreholes. It is associated with the Liquid Junction Potential created at the contact of the filtrate and the formation water, in another words, at the boundary of the invaded zone. What happens is that when two solutions of different salinities come into contact, a liquid junction electromotive force is created if the mobility of the anions and cations is not the same.
![]() Liquid junction potential
Liquid junction potential
In a sodium chloride solution the mobility of Cl- is higher than that of NaCl ions. This results in a flux of negative charges towards the less concentrated solution (generally the mud) and the creation of an electromotive force that is added to the one associated with the clay membrane.
We obtain the following relation:
|
|
with: |